H5n1 who – H5N1, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, has emerged as a global health concern. Its potential to cause severe illness and death in both humans and animals raises alarm, necessitating a thorough understanding of its characteristics, transmission, impact, and management strategies.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of H5N1, exploring its classification, genetic makeup, modes of transmission, symptoms, public health impact, surveillance and prevention measures, treatment options, vaccine development, risk communication, international collaboration, and future research directions.
H5N1 Overview
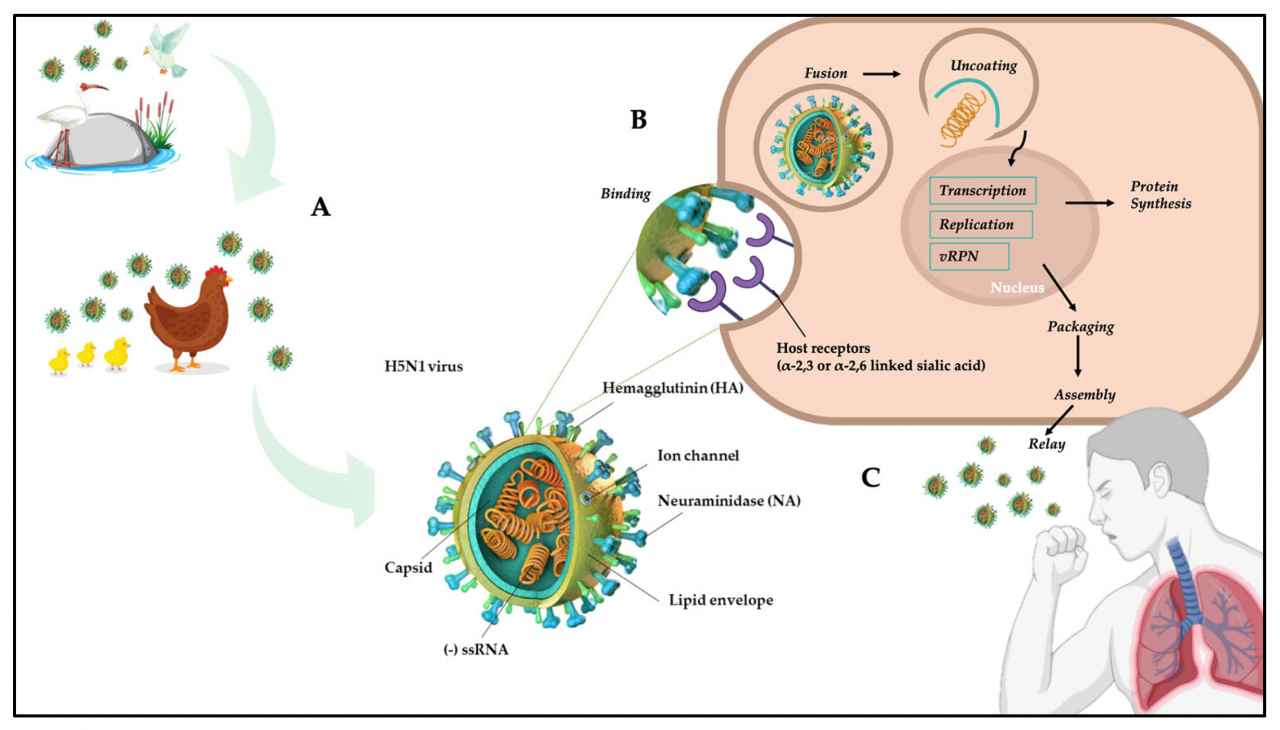
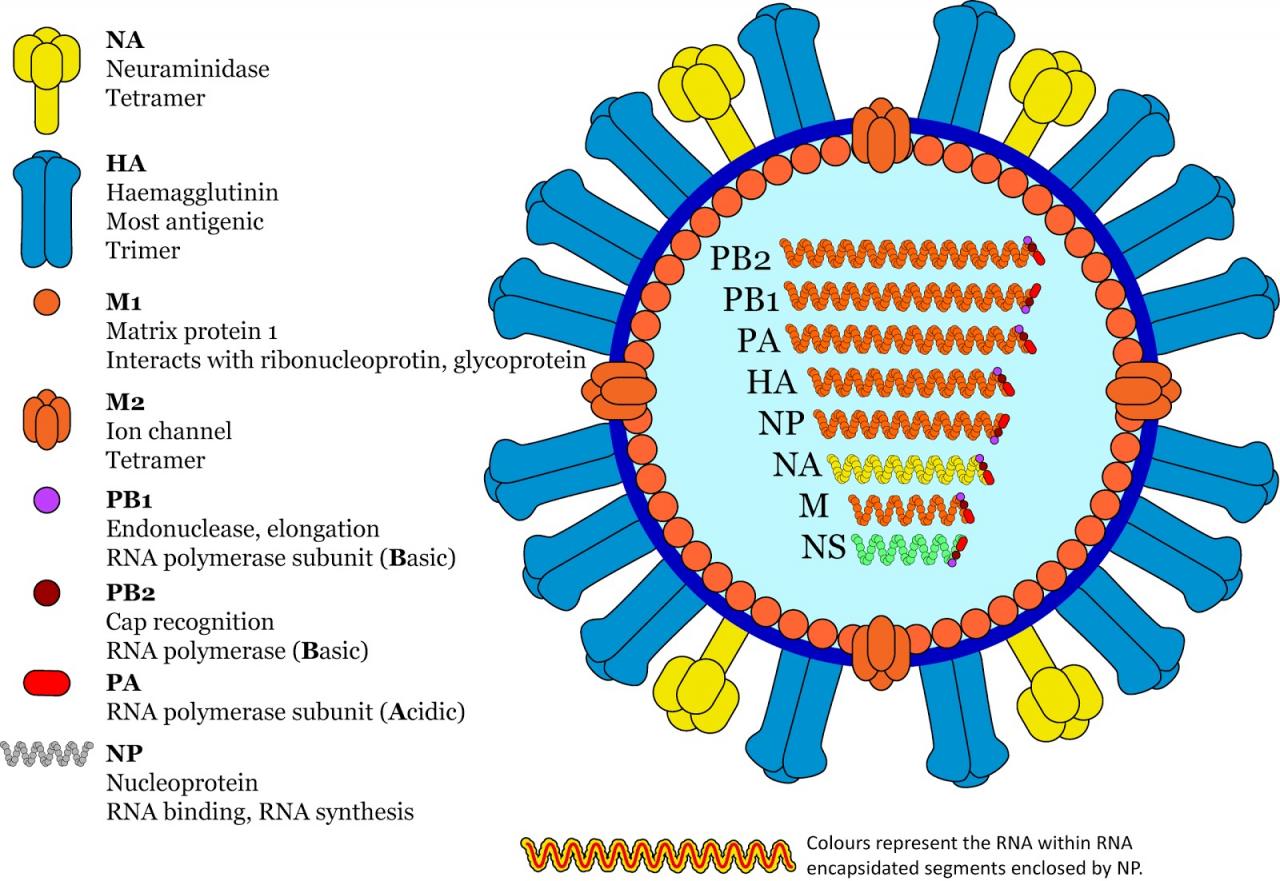
H5N1 is a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus that has caused significant concern due to its potential to infect humans and cause severe respiratory illness. It belongs to the Orthomyxoviridae family and is classified as an influenza A virus. The virus has a segmented, negative-sense RNA genome that undergoes frequent mutations, leading to the emergence of new strains.
H5N1 viruses are further classified into two main clades: clade 1 and clade 2. Clade 1 viruses are primarily associated with poultry and have been responsible for most human infections. Clade 2 viruses, on the other hand, are more diverse and have been found in both poultry and wild birds.
Some clade 2 viruses have shown increased virulence and transmissibility, raising concerns about their pandemic potential.
Transmission and Symptoms
H5N1 is primarily transmitted through contact with infected poultry or their secretions. Humans can become infected by handling infected birds, inhaling contaminated air, or consuming contaminated poultry products. The virus can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects.
Symptoms of H5N1 infection in humans can range from mild respiratory illness to severe pneumonia and respiratory failure. Common symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue. In severe cases, the virus can cause acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multiple organ failure, and death.
Public Health Impact
H5N1 outbreaks have had a significant impact on global public health. The virus has caused sporadic outbreaks in poultry and humans in various countries, leading to economic losses and public health concerns.
The case fatality rate for H5N1 infection in humans is estimated to be around 50%, making it one of the most deadly influenza viruses known. The virus has the potential to cause a pandemic if it acquires the ability to transmit efficiently from human to human.
Surveillance and Prevention
Surveillance is essential for early detection and containment of H5N1 outbreaks. Regular monitoring of poultry populations and testing of suspected cases are crucial for identifying and responding to outbreaks promptly.
Prevention measures include implementing biosecurity measures in poultry farms, vaccinating poultry, and raising awareness about the risks of H5N1 infection. Personal protective equipment (PPE) should be used when handling poultry or working in areas where the virus is known to be present.
Treatment and Vaccine Development
There are currently no specific antiviral treatments for H5N1 infection. Supportive care, including oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and antiviral drugs, are used to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Vaccine development against H5N1 is ongoing, but challenges remain in creating a vaccine that is both effective and safe. Researchers are exploring different vaccine platforms and strategies to develop vaccines that can protect against multiple strains of the virus.
Risk Communication and Education, H5n1 who
Effective risk communication and public education are crucial for H5N1 preparedness. Clear and timely information about the virus, its risks, and preventive measures should be provided to the public.
Educational campaigns should focus on raising awareness about the importance of poultry biosecurity, personal hygiene, and seeking medical attention promptly if symptoms of infection occur.
International Collaboration
International collaboration is essential for effective H5N1 surveillance, prevention, and response. Global organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) play a vital role in coordinating efforts and sharing information.
International cooperation allows for the sharing of resources, expertise, and best practices, enhancing the global capacity to respond to H5N1 outbreaks and mitigate their impact.
Future Directions
Future research on H5N1 will focus on understanding the virus’s evolution, developing effective vaccines and treatments, and improving surveillance and prevention measures.
Monitoring the emergence of new strains, studying the mechanisms of viral transmission, and exploring innovative approaches to vaccine development are key areas for future research. Continuous collaboration and information sharing among researchers and public health officials will be essential for advancing our knowledge and preparedness against H5N1.
Epilogue: H5n1 Who
As we navigate the evolving landscape of H5N1, continued research, collaboration, and public education are crucial to mitigate its impact and safeguard global health. By understanding the complexities of this virus, we empower ourselves to respond effectively and protect communities from its potential threats.